The Hollow Earth Theory stands as one of the most captivating and enduring mysteries in the realm of alternative historical and scientific beliefs. Proposing that our planet harbors a vast, habitable space within its core, this theory has fascinated thinkers, adventurers, and conspiracy theorists for centuries. In this article, we delve deep into the origins, proponents, evidence, and controversies surrounding the Hollow Earth Theory, seeking to unravel the enigma that has captured the imagination of generations.
Origins of the Hollow Earth Concept
The concept of a hollow Earth can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where myths and legends often depicted subterranean realms inhabited by gods, spirits, or mythical creatures. Due to religious convictions and interpretations of biblical texts, the concept of a hollow earth gained popularity in the Middle Ages among scholars and theologians. However, it wasn’t until the Age of Exploration and the Enlightenment that the Hollow Earth Theory began to take shape as a scientific hypothesis.
Proponents and Pioneers
One of the earliest proponents of the Hollow Earth Theory was the English astronomer and mathematician Edmond Halley, known for his work on comets and planetary motion. In the late 17th century, Halley postulated the existence of concentric spheres within the Earth, proposing that these hollow spaces could account for variations in the Earth’s magnetic field. His ideas laid the groundwork for future explorations and speculations regarding the nature of the Earth’s interior.
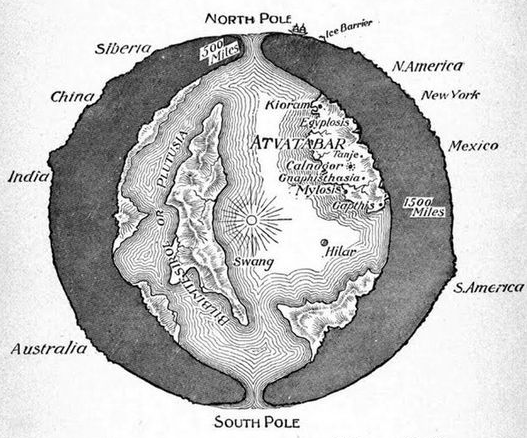
In the 19th century, the Hollow Earth Theory gained further prominence through the writings of American author and lecturer John Cleves Symmes Jr. Symmes advocated for a hollow Earth with openings at the poles, which he believed could be accessed through expeditions. While Symmes’ theories were met with skepticism by the scientific community, they captured the public’s imagination and inspired a wave of exploration and speculation.
Explorations and Expeditions
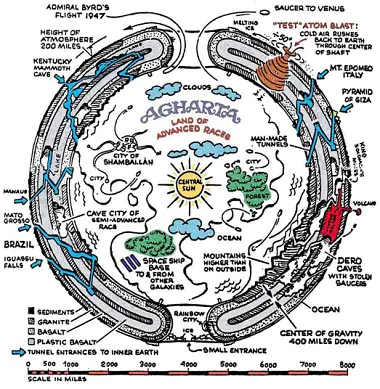
Throughout history, numerous expeditions have been launched in search of evidence supporting the Hollow Earth Theory. One of the most famous expeditions was the journey of Admiral Richard E. Byrd, a renowned American explorer and aviator. In 1926, Byrd led an expedition to Antarctica, during which he claimed to have discovered an entrance to the inner Earth at the South Pole. While Byrd’s accounts were met with controversy and skepticism, they fueled speculation about hidden realms beneath the Earth’s surface.
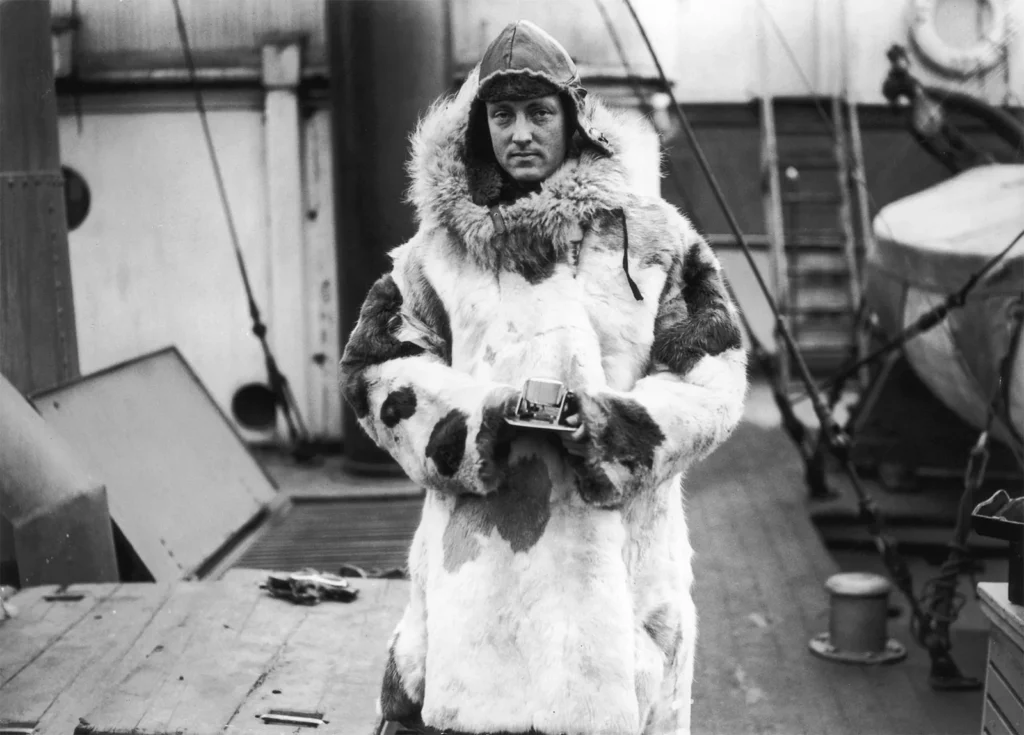

Evidence and Anomalies
Proponents of the Hollow Earth Theory point to various pieces of evidence and anomalies as proof of its validity. These include purported sightings of flying saucers emerging from the Earth’s poles, anomalous seismic readings suggesting hollow cavities within the Earth, and alleged encounters with subterranean civilizations reported by explorers and adventurers. However, skeptics argue that such evidence is anecdotal, speculative, or easily explained by natural phenomena.

Scientific Challenges and Criticisms
The Hollow Earth Theory faces significant scientific challenges and criticisms, primarily stemming from our current understanding of geology, physics, and planetary science. Modern scientific models of the Earth’s interior, based on seismic data, gravitational measurements, and geological observations, paint a picture of a solid, layered structure consistent with conventional geophysical theories. Critics argue that the concept of a hollow Earth is incompatible with established scientific principles and lacks empirical evidence to support its validity.

Contemporary Perspectives and Cultural Impact
Despite its scientific implausibility, the Hollow Earth Theory continues to captivate the popular imagination and inspire works of fiction, art, and entertainment. From literature and film to conspiracy theories and New Age beliefs, the concept of a hidden world beneath our feet persists as a potent symbol of mystery and exploration. Whether viewed as a fanciful myth or a tantalizing possibility, the Hollow Earth Theory remains a testament to humanity’s enduring curiosity about the unknown and the unexplored.

Conclusion
The Hollow Earth Theory stands as a testament to humanity’s capacity for imagination, speculation, and exploration. While it may never be proven scientifically, its enduring appeal lies in its ability to evoke wonder, curiosity, and a sense of possibility. Whether dismissed as pseudoscience or embraced as a tantalizing mystery, the concept of a hollow Earth continues to spark debate, fuel speculation, and inspire the adventurous spirit of exploration that defines the human experience.
POPULAR TODAY
The Bermuda Triangle, a region of the western Atlantic Ocean notorious for unexplained disappearances and strange occurrences, has captivated the imaginations of people worldwide
